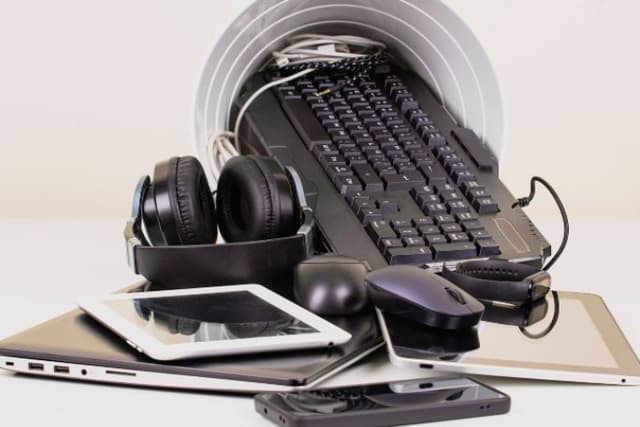

Circular Economies for Electronic Waste
Lesson1 of 4 in this unit
SecondaryYear 9 - 10TechnologyDesign and TechnologiesEnvironmentalSustainabilityEconomicDesign Thinking
Summary
Lesson Guides and Printables
Lesson Plan
Student Worksheet
Teacher Content Info

Visual Explainer

The R'S of Sustainability
