What is the Bystander Effect?
Lesson3 of 6 in this unit
SecondaryYear 9 - 10Health and Physical EducationHealthSocialEqualityHuman RightsLeadershipSocial Action
Summary
Lesson Guides and Printables
Lesson Plan
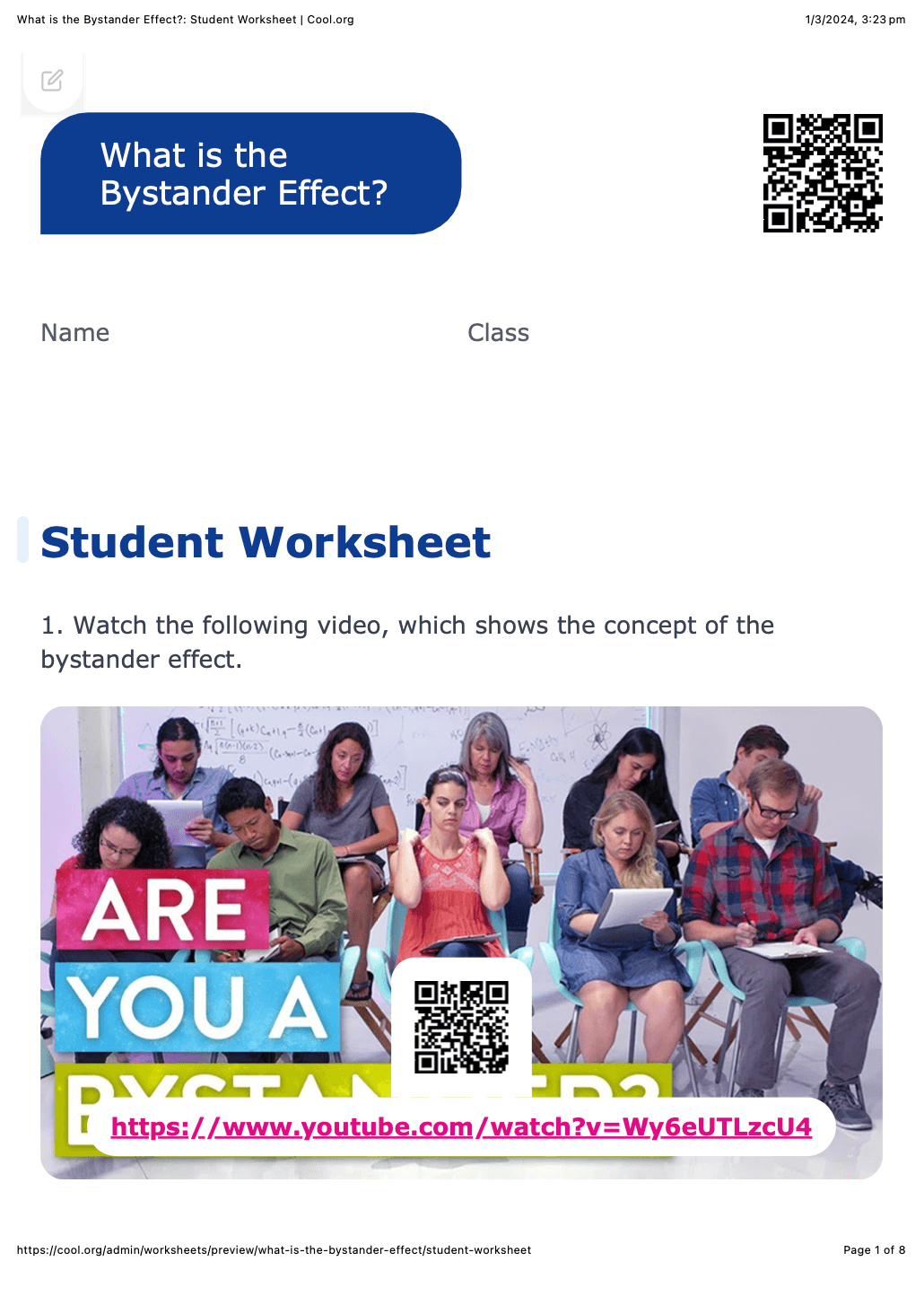
Student Worksheet
Teacher Content Info


Lesson Plan

Student Worksheet

Teacher Content Info
