
Minibeasts, Pollinators, Organics and Pesticides
Lesson6 of 11 in this unit
SecondaryYear 9Humanities and Social SciencesGeographyEnvironmentalSustainability
Summary
Lesson Guides and Printables
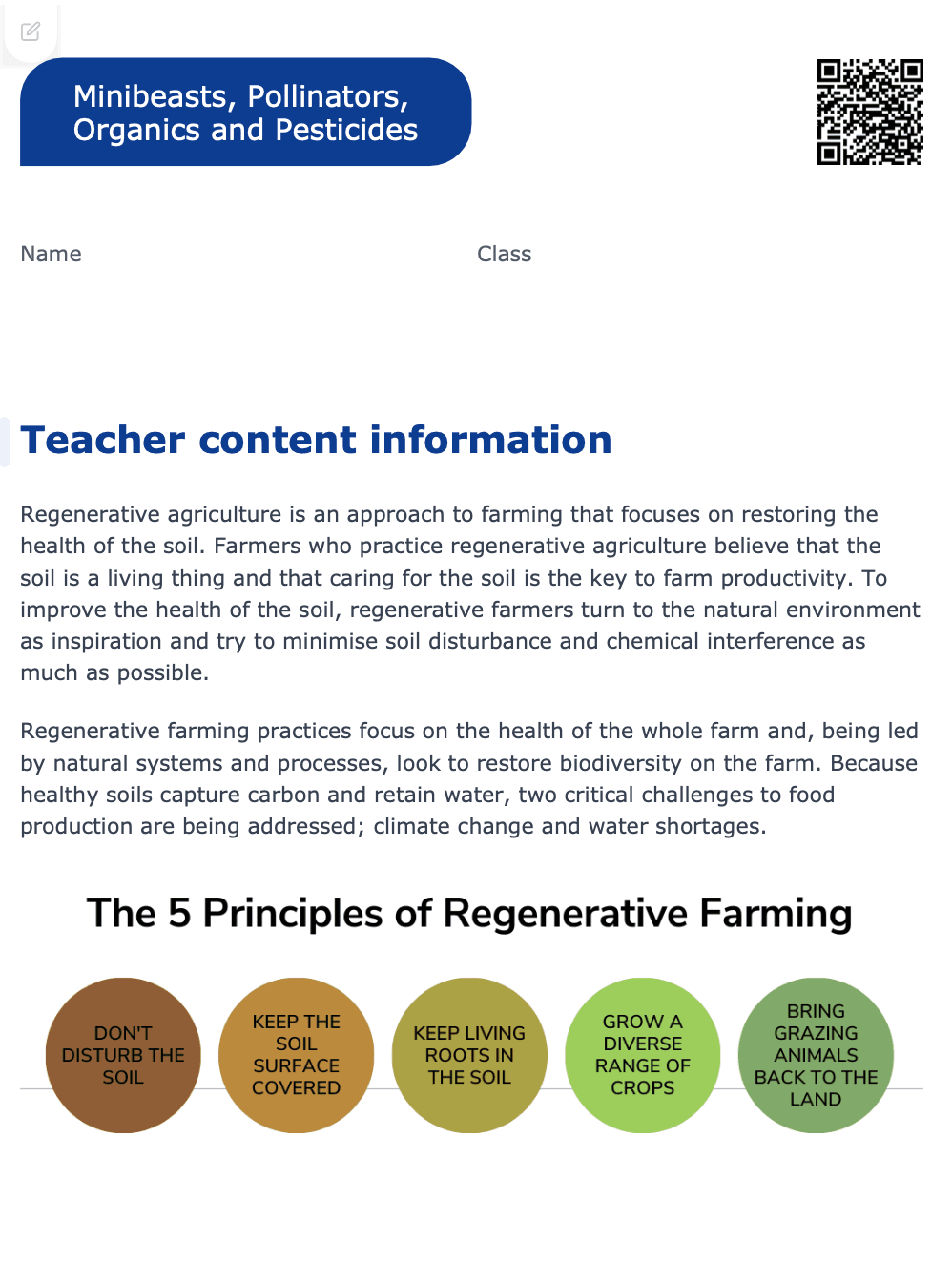
Teacher Content Information
Lesson Plan
Student Worksheet
Debate Guidelines
