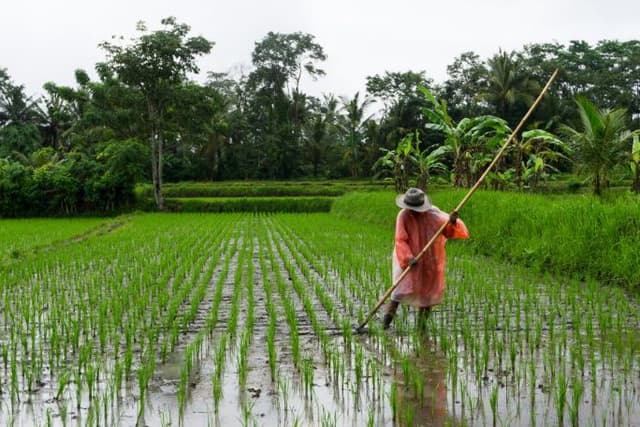

Sustainable Farming Practices in Indonesia
Lesson7 of 11 in this unit
SecondaryYear 9Humanities and Social SciencesGeographyEnvironmentalSustainability
Summary
Lesson Guides and Printables
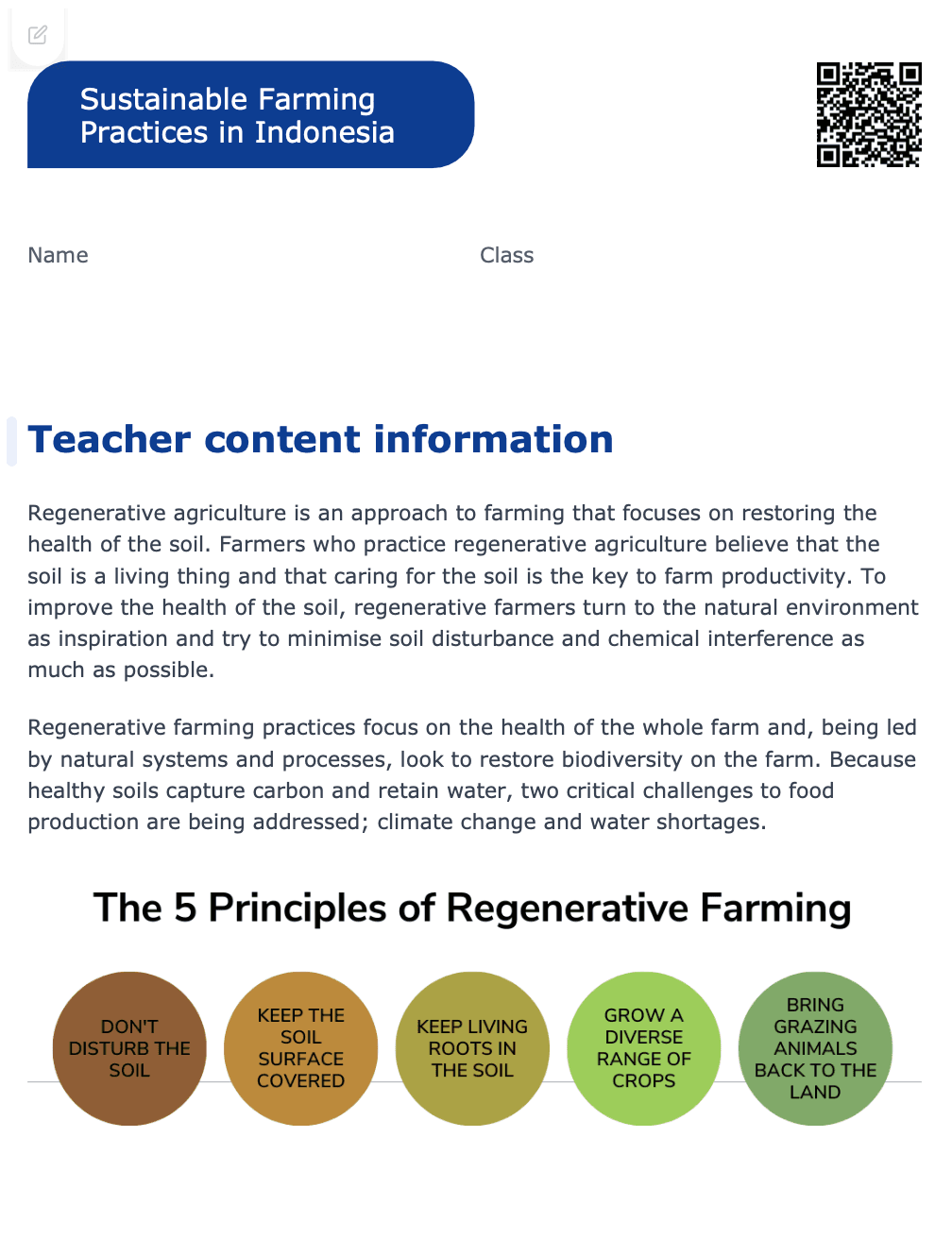
Teacher Content Information
Lesson Plan

Student Worksheet
Article - Climate Change Indonesia

Article - Indonesian Rice and Coffee Market

Article - Modern Agriculture
