Learning intentions:
Students will...
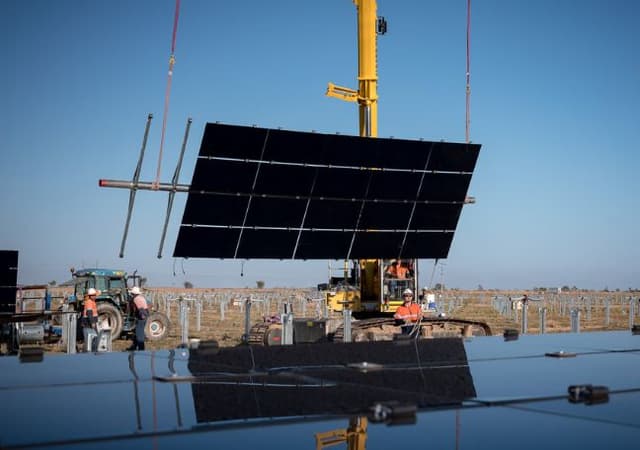
- understand how to apply trigonometry to real-world contexts by investigating the optimal direction and tilt angle for solar panels and exploring how these factors impact energy efficiency in a solar farm design.
Success criteria:
Students can...
- calculate unknown side lengths and unknown angles in right-angled triangles using trigonometry
- apply trigonometric principles to determine the height of objects using their shadow lengths and the sun’s angle of elevation in order to design a small-scale solar farm layout that maximises energy efficiency by selecting the appropriate direction and tilt angle for the panels.
- apply mathematical reasoning to a real-world context and communicate findings