Learning intentions:
Students will...
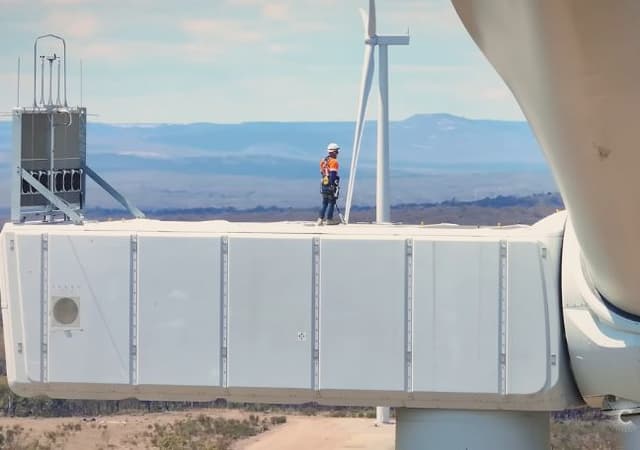
- explore the factors that influence the location and layout of wind farms, and evaluate how these considerations impact the efficiency and sustainability of renewable energy projects.
Success criteria:
Students can...
- design a wind farm layout that optimises turbine placement based on wind resource data and spacing guidelines
- evaluate the suitability of different locations for a wind farm by considering factors such as wind density, environmental impact, and proximity to transmission lines
- justify their chosen wind farm location and layout by providing specific examples and reasoning based on analysis of data.