Learning intentions:
Students will...
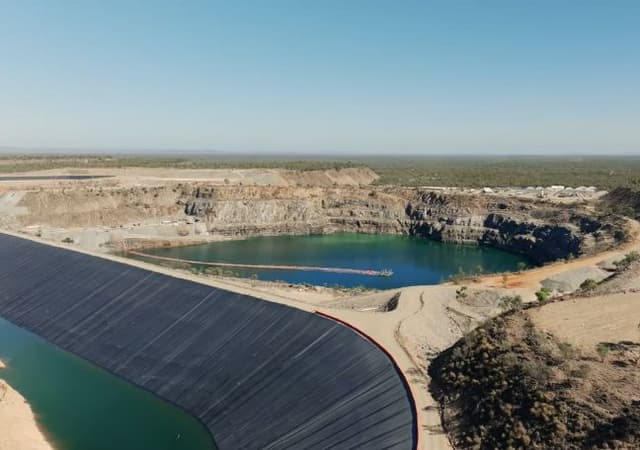
- explore the role of civil engineering in renewable energy projects such as the Kidston Pumped Hydro project
- investigate how mathematical concepts such as volume, rates, and ratios can be applied to solve real-world engineering challenges.
Success criteria:
Students can...
- calculate quantities that are directly proportional to another
- calculate the volume of a cylinder
- apply mathematical reasoning to a real-world context and present a mathematical justification for how increasing water usage in the Kidston pumped hydro project can improve energy output, using real-world data from the project.